Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-DRB 10
Chỉ tiêu phân tích:
Ứng dụng:
Phạm vi giao hàng: 1 x Refractometer 1 x Network adapter 1 x Factory calibration certificate 1 x User manual
142.274.880 ₫ £ 4,790.40
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-DRB 10
Chỉ tiêu phân tích:
Ứng dụng:
Phạm vi giao hàng: 1 x Refractometer 1 x Network adapter 1 x Factory calibration certificate 1 x User manual
Abbe refractometer for measuring refractive index and % Brix / Thermostat connection / Large touch screen / Data memory for 100 values / 8-digit ID assignment for users and samples / RS-232 interface
The Abbe Digital Refractometer is easy to use and requires only a small amount of sample. The digital screen avoids reading errors. You can save the results in the memory of the Abbe refractometer, print them or download them to a computer. The ability to assign eight-digit user and sample names via the Abbe refractometer menu facilitates subsequent analysis of measurement results. For each measurement, the temperature is indicated on the touch screen of the Abbe refractometer, which makes it possible to convert the values which depend on the temperature.
Principle of measurement of the Abbe digital refractometer
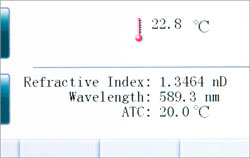 With the Abbe refractometer, you can accurately determine the refractive index and the Brix value. The refractive index relates the wavelength of light in vacuum to the wavelength of light used in the medium being tested. A high-resolution sensor built into the refractometer measures the total reflectance of a special light source, with a wavelength of 589 nm, when the light reflects off the sample to be checked. Therefore, the Abbe refractometer is indicated for measuring liquid, viscous and solid samples. The measurement does not depend on the turbidity, viscosity, transparency or absorption of a sample. After the measurement is completed, the Abbe refractometer displays the refractive index between 1.3000 and 1, 7000 nD and the Brix value between 0 and 100%. In addition to measuring these parameters, the Abbe refractometer has high resolution and precision. Thanks to the various settings in the menu, it is possible to adapt the Abbe refractometer to the needs and requirements of the user. You can make all settings on the easy-to-read touchscreen.
With the Abbe refractometer, you can accurately determine the refractive index and the Brix value. The refractive index relates the wavelength of light in vacuum to the wavelength of light used in the medium being tested. A high-resolution sensor built into the refractometer measures the total reflectance of a special light source, with a wavelength of 589 nm, when the light reflects off the sample to be checked. Therefore, the Abbe refractometer is indicated for measuring liquid, viscous and solid samples. The measurement does not depend on the turbidity, viscosity, transparency or absorption of a sample. After the measurement is completed, the Abbe refractometer displays the refractive index between 1.3000 and 1, 7000 nD and the Brix value between 0 and 100%. In addition to measuring these parameters, the Abbe refractometer has high resolution and precision. Thanks to the various settings in the menu, it is possible to adapt the Abbe refractometer to the needs and requirements of the user. You can make all settings on the easy-to-read touchscreen.
The Abbe refractometer is a device that uses the laws of optics to determine the refractive index. Light can be diffracted, reflected or absorbed while passing from one medium to another. This Abbe refractometer uses the principle of reflection. The reflection takes place in the boundary layer between the prism and the sample. Since light does not need to pass through the sample, this Abbe refractometer performs the measurement regardless of the sample’s turbidity, viscosity or transparency.
The sample is placed in the measurement chamber of the Abbe refractometer. It is necessary to close the cover of the measuring chamber to avoid errors caused by the entry of external light. When the measurement begins, the internal light source of the Abbe refractometer sends rays of light through the prism to the boundary layer between the prism and the sample. These rays of light are completely reflected from a determined angle. The optical sensor of the Abbe Digital Refractometer detects these reflected rays. By evaluating the areas illuminated by the sensor, the Abbe refractometer calculates the refractive index of the sample. The refractive index of the prism used in the Abbe refractometer must be greater than the refractive index of the sample.
The measuring range of this Abbe refractometer is from 1.30000 nD to 1.70000 nD. The letter D indicates the wavelength of the light used during the measurement: 589.3 nanometers. The refractive index depends not only on the type of light but also on the temperature. When the temperature increases, the refractive index decreases. To obtain highly accurate results, many Abbe refractometers incorporate connecting tubing for temperature control.
Estimation of the Brix value with the Abbe refractometer
There is a direct relationship between the refractive index and the Brix value. It is for this reason that it is possible to determine, with great precision, by means of this Abbe refractometer, not only the refractive index but also the Brix value. The Brix value is the most commonly used unit for measuring sugar concentration, which is frequently determined by an Abbe refractometer. This value is defined from the sucrose of the water.
1° Brix = 1% Brix contains 100 g of 1 g sucrose solution in 99 g of water.
12° Brix = 12% Brix contains 100 g of a solution of 12 g sucrose in 88 g of water.
Frequently the Brix value is used as a test value – also for sugar-free samples – because it is easier to compare than the refractive index. For example, at a measurement temperature of 20 ºC:
2% Brix = 1.33586 nD, 12 % Brix = 1.35093 nD, 30 % Brix = 1.38115 nD and 60 % Brix = 1.44193 nD.
Calibration and adjustment of the Abbe refractometer
Each time the Abbe refractometer is turned on, a calibration is automatically performed. Calibration ensures error-free measurement. The device itself calibrates completely automatically. It is also possible to perform a calibration at any time. If you wish to obtain an ISO or DAkkS calibration certificate, you can send the Abbe refractometer to an accredited metrology laboratory, which calibrates the device using certified standards and issues a calibration certificate for the Abbe refractometer. This certificate allows you to accredit the accuracy and the calibration interval.
There are standard solutions with different refractive indices that allow the user to control the accuracy of the Abbe refractometer. If the measurement results have a lot of deviations, although the temperature has been checked, you can adjust the Abbe refractometer. To do this, you must enter the Abbe refractometer calibration menu and enter the refractive index of the solution used. The Abbe refractometer will be set to the value of this standard solution.
Recording of data in the Abbe refractometer
It is possible to download the measured values of the Abbe refractometer via the RS-232 interface to a computer or to save this data directly in the Abbe refractometer. For later analysis, you can retrieve values on the Abbe Refractometer touch screen by sample number, user number or date. You can also download these values to another data carrier. It is also possible to read the measurement values by means of the PC software, which will help to edit the additional documentation. The Abbe refractometer also allows to filter the saved values by date, by user number or by sample number. To avoid measurement errors caused by ambient light sources, such as daylight, light bulbs, etc., it is necessary to close the cover located in the upper part of the Abbe refractometer. Knowing that the refractive index depends on the temperature and that it is necessary to take it into account to obtain an accurate measurement, it is important that the ambient temperature is constant. A temperature of around 20 ºC is perfect.
If you want to measure a substance at boiling temperature, the control temperature will no longer be necessary. The unit used to indicate the refractive index is nD. The letter “D” indicates the reference wavelength of the light source, which refers to the D line of sodium at 589 nm. Due to the wavelength dependence of the refractive index, the measurement must be made with monochromatic light. In some cases, the temperature at which the measurement was made is also indicated as an exponent value, which allows better traceability of the ambient conditions during the measurement.
Abbe refractometer software for computer
You can retrieve values from the memory of the Abbe refractometer using the corresponding PC software. The values transferred via the RS-232 interface of the Abbe refractometer appear in tabular form. You can export all or part of this data as a CSV file. The table contains:
No. / Date / Time / User identification / Sample identification / Measured value / Unit nD or %Brix / Measurement temperature.
The software also allows you to erase the memory of the Abbe refractometer. Thus you will again have 100 positions and this will avoid recovering twice a value.
Abbe refractometer accessories for special liquids
In order to avoid measurement errors caused by the entry of external light, it is necessary to close the cover of the measurement chamber of the Abbe refractometer. This Abbe refractometer offers some special covers for particular liquids. The cover for high viscosity liquids presses the sample by means of the additional element installed on the prism surface of the Abbe refractometer. The lid for volatile samples is fitted with a sealing ring, which prevents liquid evaporation during temperature compensation and measurement in the Abbe refractometer. Evaporation would cause a change in the concentration of the sample to be measured and, therefore, an incorrect result.
 Abbe refractometers are widely used as they allow quick and easy measurement of refractive index. The refractive index is often used to check the purity of a substance. In the case of many mixtures of two substances, there is an obvious correlation between refractive index and composition. That is why the Abbe refractometer makes it easy to determine the content of a specific substance in a solvent, using the refractive index. In the case of mixtures of substances which are subject to certain fluctuations like, for example, honey with different water contents, a range can be given for the desired refractive index. Adherence to these values can be checked using the Abbe refractometer.
Abbe refractometers are widely used as they allow quick and easy measurement of refractive index. The refractive index is often used to check the purity of a substance. In the case of many mixtures of two substances, there is an obvious correlation between refractive index and composition. That is why the Abbe refractometer makes it easy to determine the content of a specific substance in a solvent, using the refractive index. In the case of mixtures of substances which are subject to certain fluctuations like, for example, honey with different water contents, a range can be given for the desired refractive index. Adherence to these values can be checked using the Abbe refractometer.
The Abbe refractometer in the chemical, automotive, metallurgical and construction industries determines concentrations of solvents, stripping agents, industrial oils, lacquers, adhesives, surfactants, coolants and checks chemical processes during production.
The Abbe refractometer in the sugar, food and beverage industry is used to determine the sugar content of intermediate and finished products, the alcohol content of beer, wine, spirit drinks, in quality control and wastewater control.
The Abbe refractometer in medicine and pharmacy allows the rapid analysis of body fluids, the control of the purity of raw materials, intermediate and finished products such as, for example, infusion solutions or preparations for dialysis.
Estimates of the concentration of raw materials, auxiliary and operating materials, as well as semi-finished and finished products are made. Verification of solids content is extremely important in many industries, whether for development, research or production. This verification is usually done with an Abbe refractometer. In the beverage industry, monitoring sugar content and concentration is a very important measurement and, therefore, part of routine analysis.
Many applications aim to determine the concentration in a carrier medium. A typical example is to calculate the sugar content in mostly aqueous solutions. For example, by measuring the sugar concentration of a grape, it is possible to determine its degree of maturity, which is very interesting for winegrowers. The Abbe refractometer can also be used to measure the original wort when making beer or the water content of honey. In industry, the Abbe refractometer makes it possible, for example, to determine the oil-water concentration in the refrigerant emulsion mixtures of metalworking machines or the acid concentration of batteries. In medicine, it is used, for example, to calculate the protein content of urine. In many other applications, a refractometer is useful and makes the job easier. To guarantee the comparability of the results, adapted scales have been established: degrees Oechsle, Brix and Plaque). Most refractometers are equipped with a double scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe or the triple scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe/KMW-Babo. Internationally, the scale in %: sucrose (Brix) is valid. The Oechsle scale 0-140°Oe is valid for fruit juices, foreign grape musts and purees from distillation. For German grape musts, the Oechsle scale 30-140°Oe is the only valid one. Refractometers with this scale are marked with a “D”. adapted scales have been established: Oechsle, Brix and Plaque degrees). Most refractometers are equipped with a double scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe or the triple scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe/KMW-Babo. Internationally, the scale in %: sucrose (Brix) is valid. The Oechsle scale 0-140°Oe is valid for fruit juices, foreign grape musts and purees from distillation. For German grape musts, the Oechsle scale 30-140°Oe is the only valid one. Refractometers with this scale are marked with a “D”. adapted scales have been established: Oechsle, Brix and Plaque degrees). Most refractometers are equipped with a double scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe or the triple scale in %: sucrose (Brix)/°Oe/KMW-Babo. Internationally, the scale in %: sucrose (Brix) is valid. The Oechsle scale 0-140°Oe is valid for fruit juices, foreign grape musts and purees from distillation. For German grape musts, the Oechsle scale 30-140°Oe is the only valid one. Refractometers with this scale are marked with a “D”. sucrose (Brix) is valid. The Oechsle scale 0-140°Oe is valid for fruit juices, foreign grape musts and purees from distillation. For German grape musts, the Oechsle scale 30-140°Oe is the only valid one. Refractometers with this scale are marked with a “D”. sucrose (Brix) is valid. The Oechsle scale 0-140°Oe is valid for fruit juices, foreign grape musts and purees from distillation. For German grape musts, the Oechsle scale 30-140°Oe is the only valid one. Refractometers with this scale are marked with a “D”.
To meet and maintain your company’s internal quality control criteria or defined calibration intervals, you can send the Abbe refractometer to the PCE Instruments metrology and calibration laboratory at any time. The Abbe refractometer is calibrated using certified standards. At the same time, an ISO calibration certificate is issued, which allows you to comply with the specifications indicated in the data sheet of the device and to be able to demonstrate the accuracy of the measurement. You can also request standards with different refractive indices that allow you to periodically check the accuracy of the refractometer.
The Abbe PCE-DRB 10 refractometer is a modern, inexpensive, high-precision, data-logging measuring instrument. It is a device indicated for a multifunctional analysis of different parameters such as the refractive index or the Brix value. All this makes it an indispensable tool for any private and public laboratory working in the field of analysis.
How does an Abbe refractometer work?
An Abbe refractometer is a measuring instrument for determining refractive index. This works for both liquid and solid materials, as long as they are transparent and using the refraction method. Once the sample has been placed or used in the Abbe refractometer, a special optical system generates two opposing fields, one light and one dark. The boundary line between the two fields is the result of the sample measurement.
Im Groben kann man zwischen drei Messverfahren von einem Abbe Refractometer unterscheiden:
Broadly speaking, three measurement methods can be distinguished in a refractometer:
– transmitted light
– grazing incidence
– Total reflection
For this, refraction is used, that is, the refraction or total reflection of light and the physical properties of these. The common denominator of the three measuring principles presented is the measuring prism with known refractive index. One of the properties of light is that it does not travel at the same speed in the transition between the measuring prism and the medium of the sample, but that it propagates at a different speed. The unknown refractive index of the medium to be measured is calculated by means of the deviation of the light.
– When the principle of transmitted light is used, a parallel beam of rays refracts in the boundary layer.
– With grazing incidence and total reflection, the critical angle of a beam of rays with different angles of incidence is measured in the boundary layer.
The most accurate measurement is obtained at 20°C, which is why the temperature must always be determined and the distortion specified using a correction table. But there are also refractometers equipped with automatic temperature correction, which of course increases the comfort of measurement enormously.
Abbe number
The classification of glasses (eg spectacle lenses or engineering plastics) is done, for example, by means of the Abbe number. This number owes its name to its inventor Ernst Karl Abbe (Jena), and is used to classify glasses. Simply put, the Abbe number represents the ratio of the scattering of light at different wavelengths to the corresponding refractive index (change in refractive index with respect to wavelength). The number also characterizes the dispersion of the glass. The higher the dispersion, the smaller the Abbe number. There is a clear relationship between the quality of the glass and the Abbe number: High number = high quality. The dispersion of plastics is also determined by an Abbe refractometer.
Tổng số người xem bài viết: 235
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-AC500G
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-AC500G
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VT 3700
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VT 3700
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VM 3D
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VM 3D
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VDL 24I
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VDL 24I
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VS12
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VS12
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-PVS 10
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-PVS 10
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VDR 10-ICA
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-VDR 10-ICA
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-AC420-1610-A
Hãng sản xuất: PCE - ANH
Model: PCE-AC420-1610-A

Đánh giá
Chưa có đánh giá nào.